How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both beginners and experienced pilots. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety regulations to mastering drone controls, optimizing camera settings, and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll explore the intricacies of flight modes, battery management, and essential maintenance procedures, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge to capture stunning aerial footage responsibly.
We will delve into the specifics of various drone models and their unique functionalities, while also emphasizing the importance of adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions to ensure safe and legal operation. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the necessary skills and understanding to navigate the exciting world of drone piloting with ease and confidence.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding and adhering to local regulations, and assessing environmental conditions. Failure to do so can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, or legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is essential to identify any potential problems before takeoff. The following table Artikels key areas to check:
| Item | Check | Status (Pass/Fail) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or imbalance. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Motors | Check for any visual damage or loose connections. Ensure they spin freely. | Listen for unusual noises during a motor test. | |
| Battery | Verify battery level and ensure it is securely connected. Check for any signs of damage or swelling. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. | |
| Camera | Check lens for dirt or smudges. Confirm camera functionality. | Clean the lens gently with a microfiber cloth. | |
| GPS Signal | Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. | Allow sufficient time for GPS acquisition. | |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | Ensure the gimbal is properly calibrated. | |
| Remote Control | Verify battery level and proper connection with the drone. | Check for any loose connections or damaged components. | |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage to the drone body. | Note any dents, scratches, or cracks. |
Understanding Local Drone Regulations
Operating a drone requires awareness of and adherence to local laws and regulations. These regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure safety and prevent interference with other airspace users. Examples of regulatory bodies include the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) in the United Kingdom, and Transport Canada in Canada.
These bodies define airspace restrictions, licensing requirements, and operational limitations, such as flight altitude and proximity to airports.
Safe Flight Decision-Making Flowchart, How to operate a drone
A systematic approach is crucial to determine if it is safe to fly. The following flowchart helps to assess weather conditions and other environmental factors.
[A descriptive explanation of a flowchart would be included here. The flowchart would visually represent a decision-making process, starting with checking wind speed, then proceeding to visibility, precipitation, and finally, determining if it is safe to fly or not. Each decision point would have clear yes/no branches leading to the final outcome.]
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
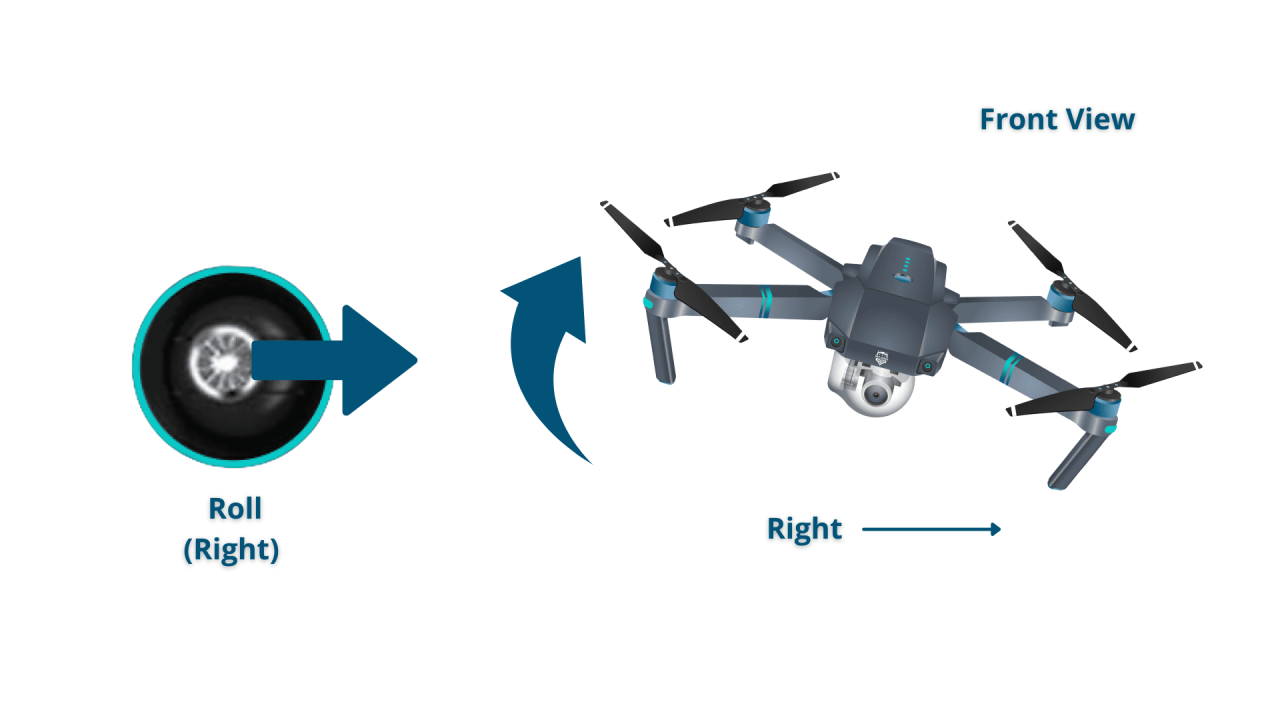
Understanding the drone’s controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers the functions of the remote control, different flight modes, and basic maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions
A standard drone remote typically includes two control sticks and several buttons. Each control affects the drone’s movement in a specific way:
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): The left stick controls the drone’s altitude (throttle) and rotation (yaw). Pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases altitude. Rotating the stick left or right causes the drone to rotate around its vertical axis.
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): The right stick controls the drone’s pitch (forward and backward movement) and roll (side-to-side movement). Pushing the stick forward moves the drone forward, pushing it backward moves it backward. Pushing the stick left or right causes the drone to tilt and move sideways.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cuts power to the motors, causing the drone to fall.
- Camera Control Buttons: These buttons allow for adjustments to camera settings such as zoom and photo/video recording.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and maneuverability. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots. GPS mode utilizes GPS signals for improved positioning and stability, particularly useful for longer flights.
Performing Basic Drone Maneuvers
This step-by-step guide details basic drone maneuvers:
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate takeoff. Maintain a steady hand and monitor the drone’s ascent.
- Hovering: Once airborne, maintain a stable position by keeping the left stick centered. Minor adjustments may be needed to maintain altitude and position.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use the right stick to control the drone’s movement forward, backward, left, and right. Gentle movements are recommended, especially for beginners.
- Landing: Gently push the left stick downwards to initiate a controlled descent. Land the drone smoothly on a flat, stable surface.
Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
Achieving high-quality aerial footage requires understanding and utilizing the drone’s camera settings effectively. This section discusses camera settings and techniques for optimal image capture in various lighting conditions.
Achieving Stable and High-Quality Footage
Several factors contribute to stable and high-quality aerial footage. Using a gimbal for camera stabilization is crucial. Maintaining smooth, controlled movements prevents blurry footage. Understanding camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture further enhances image quality.
| Setting | Description | Effect on Image | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. | Higher ISO increases sensitivity but can introduce noise. | Start with the lowest ISO possible for your lighting conditions. |
| Shutter Speed | Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. | Faster shutter speeds freeze motion but require more light. Slower speeds blur motion but allow for lower light shooting. | Experiment to find the optimal balance between sharpness and motion blur. |
| Aperture | Controls the size of the lens opening. | Wider apertures (lower f-numbers) let in more light but reduce depth of field. Narrower apertures (higher f-numbers) increase depth of field but require more light. | Adjust based on desired depth of field and lighting conditions. |
| White Balance | Adjusts the color temperature of the image. | Improves color accuracy. | Select the appropriate setting for the lighting conditions (e.g., sunny, cloudy, shade). |
Adjusting Camera Settings for Various Lighting Conditions
Optimal camera settings vary depending on lighting conditions. In bright sunlight, a lower ISO and faster shutter speed are usually recommended to prevent overexposure. In low-light conditions, a higher ISO and slower shutter speed might be necessary to capture sufficient light, though this may introduce noise. White balance adjustments are crucial for accurate color reproduction in all lighting scenarios.
Battery Management and Flight Time Optimization
Proper battery care and management are crucial for extending the lifespan of drone batteries and maximizing flight time. This section covers battery maintenance, flight time calculations, and best practices for extending flight duration.
Proper Battery Care and Maintenance
To extend battery lifespan, store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid fully charging or fully discharging batteries repeatedly. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
Calculating Flight Time
Flight time depends on several factors, including battery capacity (mAh), drone model, and flight style. A general estimate can be obtained by dividing the battery capacity by the drone’s average current draw. However, actual flight time may vary due to environmental conditions and flight maneuvers. For example, a drone with a 5000mAh battery and an average current draw of 10A might have a theoretical flight time of 30 minutes (5000mAh / 10A = 30 minutes).
This is just an approximation, and real-world flight time may be shorter.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone piloting is crucial for both personal safety and the protection of others.
Best Practices for Maximizing Flight Time
Several practices can help maximize flight time:
- Minimize aggressive maneuvers.
- Avoid flying against strong winds.
- Utilize power-saving modes.
- Avoid unnecessary hovering.
- Keep the drone’s weight as light as possible.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues

Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is essential for maintaining operational readiness. This section addresses troubleshooting steps for various issues.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Proper training ensures responsible drone usage and helps you avoid potential hazards.
Identifying and Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Several common problems may arise during drone operation. These issues and their troubleshooting steps are described below:
- Low Battery: Check the battery level and charge it if necessary. Consider minimizing flight time or using power-saving modes.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear skies and a strong GPS signal. Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. Check for any obstructions.
- Motor Malfunction: Inspect motors for damage or loose connections. Try recalibrating the drone’s ESCs (Electronic Speed Controllers).
- Gimbal Malfunction: Ensure the gimbal is properly calibrated. Check for any obstructions or damage to the gimbal.
- Remote Control Issues: Verify battery level and proper connection. Check for interference from other electronic devices.
Interpreting Error Messages
Error messages displayed on the drone or remote control provide valuable diagnostic information. Consult the drone’s manual for explanations of specific error codes. These messages often indicate the nature and location of the problem, guiding troubleshooting efforts.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are vital for preserving the drone’s functionality and lifespan. This section details a maintenance schedule and cleaning procedures.
Regular Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include:
- Weekly Inspection: Check for loose parts, damage, and general wear and tear.
- Monthly Cleaning: Clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens.
- Quarterly Calibration: Calibrate the compass, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and ESCs.
- Annual Service: Consider professional servicing for more in-depth checks and maintenance.
Proper Cleaning Methods
Clean the drone body with a soft, damp cloth. Use a microfiber cloth to clean the camera lens gently. Clean the propellers carefully, avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Use compressed air to remove dust and debris from hard-to-reach areas.
Safe Drone Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry, and safe location, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep it away from children and pets. Proper storage prevents damage and ensures longevity.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By understanding pre-flight procedures, drone controls, camera settings, and maintenance routines, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and respect the airspace around you. With consistent practice and a commitment to safe flying, you’ll be capturing stunning aerial imagery in no time.
Safe flying!
Top FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How do I obtain a drone pilot license or registration?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific licensing or registration requirements.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function. If available, activate it. If not, carefully bring the drone back manually, keeping it within visual range.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly.
